In this post we will study about “QUEUE” and its application.
“QUEUE”
- Like stack queue is a linear structure.
- which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed.
- The order is First In First Out (FIFO).
- Unlike stacks, a queue is open at both its ends.
- One end is always used to insert data (enqueue) and the other is used to remove data (dequeue).
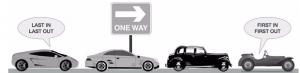
Examples of QUEUE:
- examplee of queue can be a single-lane one-way road where the vehicle enters first exits first.
- queue at the ticket windows and bus-stop.

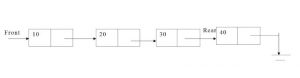
Operations on Queue:
There are 4 type of operation performed in queue:
- Enqueue
- Dequeue
- Front
- Rear.

ENQUEUE:
- The word means add an item to the queue.
- If the queue is full, then it is said to be an Overflow condition.
Algorithm for enqueue operation:
1. Create a new node
ptr=(qType*)malloc(sizeof(qType))
2. Assign the item to info
set ptr->info = item
3. Adjust ptr
set ptr->next= NULL
4. Check for existing queue
if ( rear==NULL)
{
set rear=ptr
set front=ptr
}
else goto 5.
5. Adjust rear pointer
Set rear -> next =ptr
Set rear= ptr
6.exit
before enqueue

after enqueue
CODE:
int enqueue(int data)
if(isfull())
return 0;
rear = rear + 1;
queue[rear] = data;
return 1;
end procedure
DEQUEUE:
- Removes an item from the queue.
- The items are popped in the same order in which they are pushed.
- If the queue is empty, then it is said to be an Underflow condition.
Algorithm for dequeue operation:
1. Check if queue is Empty
if (front==NULL)
display “Stack Empty ” and exit else goto 2
2. Set temp=front
3. Adjust fron
front=front->next
4. Display temp->info
5.Free(temp)
6.Exit
before dequeue
after dequeue

code
int dequeue()
{
if(isempty())
return 0;
int data = queue[front];
front = front + 1;
return data;
}
FRONT:
- Get the front item from queue.
Code:
int peek() {
return queue[front];
}
REAR:
- Get the last item from queue
code:
bool isempty() {
if(front < 0 || front > rear)
return true;
else
return false;
}